Foetal Alcohol Spectrum Disorders
Order Instructions:
Case Report -Foetal Alcohol Spectrum Disorders
Case: Leena Kerama
Leena is a 26 year old women of Aboriginal decent. She has been admitted to the
mental health unit with a diagnosis of severe alcohol use disorder (DSM V 303.0, ICD10
F10.20) and alcohol-induced depressive disorder (DSMV 291.81). Leena’s past medical
history reveals a 10 year history of severe alcohol dependence consuming an average of
8 to 10 standard drinks of alcohol (wine or beer) per day (which continued during
pregnancy) and a two year history of symptoms of depression (low mood and diminished
interest or pleasure in all or almost all activities) associated with alcohol consumption.
Leena gave birth to a baby boy (Mani) six months ago.
Leena
a) Description of severe alcohol use disorder (DSM V 303.0, ICD10 F10.20) and alcohol-induced depressive disorder (DSMV 291.81)
b) Pathophysiology – the effect alcohol has on the adult brain
c) Signs and Symptoms
d) Contemporary treatment (pharmacological and non-pharmacological)
e) Nursing management within the multidisciplinary care team
f) Treatment outcomes
SAMPLE ANSWER
Introduction
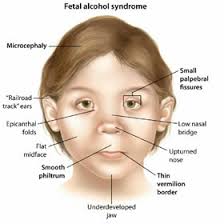
Fetal alcohol spectrum disorder (FASD) is used to refer to a condition that occurs from adverse effects on development especially when alcohol is taken during pregnancy. FASD is a brain disorder that comes with physical abnormalities. According to recent studied FASD is estimated to occur in 1 out of 100 live births but the numbers are higher in areas or communities that alcohol consumption are high (Asia News Monitor, 2015).
FASD is associated with primary disabilities that are directly from toxic effects of alcohol changing cell development. FASD conditions usually affect the nervous system and the brain since the organs are always under construction throughout pregnancy. Therefore the effect on the brain and nervous system leads to lifelong functional, emotional and cognitive difficulties (Asia News Monitor, 2015).
Excessive drinking especially taking 4 or more units per occasion may increase the risk of physical problems and unusual facial features during pregnancy especially in the first trimester. FASD can lead to secondary disabilities including mental health disorder social problems and educational (Asia News Monitor, 2015).
- Description of severe alcohol use disorder (DSM V 303.0, ICD10 F10.20) and
Alcohol-induced depressive disorder (DSMV 291.81)
Alcohol Withdrawal is a diagnosis in DSM-5 which might be a life-threatening condition found in people who drink heavily over a period of time, but they then stop or dramatically decrease their alcohol consumption. The consumption period vary from weeks, months or years.
The more the individual drinks during this time, the more likely it is for alcohol withdrawal symptoms to manifest. The manifested symptoms are usually found in adults but may occur among children and youths. The manifestations of alcohol symptoms show the level of addiction.
- Pathophysiology – the effect alcohol has on the adult brain
An acute effect of alcohol on human brain has been studied and has helped in rationalizing the development of psychotropic drugs that will assist in treating adverse effects of alcohol.
Alcohol is an addictive drug that stimulates the release of neurotransmitter dopamine from cells that originates in ventral tegmental area of the brain (VTA). THE VTA is associated with behavioral motivation and reward where if exposed to alcohol, dopamine is released into the nucleus known to reinforce drinking behaviors or make the drinking experience more enjoyable (Ritchie & Timothy & Corley & Geraldine & Davies, G., et al, 2014).
Excessive consumption of alcohol also affects the balance between excitatory and inhibitory neurotransmitters. This is because Electrochemical activation of neurons is controlled by the two hence alcohol consumption will inhibit ion flow between excitatory and inhibitory neurotransmitters leading to the imbalance (Ritchie & Timothy & Corley & Geraldine & Davies, G., et al, 2014).
The hippocampus is responsible for memory and learning and alcohol consumption reduces the size of the hippocampus. Alcohol consumption usually affect the hippocampus since its sensitive and contact with alcohol is poisonous to the nerve cells leading to damage to the cell. This therefore may lead to memory lose or may hinder learning altogether (Prakash & Neelu & Amool & et al, 2015).
Adverse consumption of alcohol may lead to lifelong problems including poor impulse control, which leads to unsafe sexual activity and unexpected bouts of violence. An individual may also experience memory loss, blackouts and poor retention of information (Lital & David & Harold, 2013).
An individual may experience permanent inability to walk straight. This because the part of the brain controlling balance is sensitive to alcohol hence continuous consumption may lead to permanent disability especially when the condition cannot be treated anymore (Prakash & Neelu & Amool & et al, 2015).
- Signs and Symptoms
Alcohol use disorder ranges from mild, moderate or severe, depending on the number of symptoms one is experiencing. They include:
- Inability to limit amount of alcohol intake
- Having strong urge to drink alcohol
- Spending a lot of money buying alcohol
- Failing to do regular obligations including going to work, school or even going home
- Continuing to drink alcohol even when one know it’s causing physical, social or interpersonal problems
- Withdrawing from interacting with other people or reducing social activities including hobbies
- Experiencing withdrawal symptoms such as sweating, shaking and nausea when one is not drinking (Asia News Monitor, 2015).
- Contemporary treatment (pharmacological and non-pharmacological)
Treatment of alcohol use disorder is done using the 30-60 days approach where patients attend 2-3 sessions per week and are encouraged to abstain from talking alcohol while other will be given prescription to help them recover. Thereafter the patient enters the continuing care phase where they attend self-help meetings. Contemporary treatment therefore combines the traditional abstinence and staying sober approach with developed drugs to assist alcohol user to completely stop taking alcohol (Mental Health Business Week, 2015).
Patients with mental illness and those dependent on alcohol consumption should be given more care or be treated with professional multidisciplinary team to ensure that they are able to recover (Dennis & Victor & Mady & Brendan, 2013).
- Nursing management within the multidisciplinary care team
Patients are usually monitored at least twice per week once they begin the detoxification program by a specialist nurse. The monitoring can be face to face or can be done through the phone. Alcohol content in the body will be taken frequently using urine drug-screening monitor. If any alcohol substance is detected the individual is discontinued from the program or they can start all over (Picci & Francesco & Marco, et al, 2014)
After the detoxification program a follow up treatment should be conducted by the specialist nurse to avoid patients from relapsing. Individual who fears that they may relapse should be given medication to prevent them from relapsing (Kattimani & Bharadwaj, 2013).
- Treatment outcome
Most patients after undergoing alcohol detoxification usually recover from the disorder. However a few of them may relapse especially when they indulge in company that takes alcohol. This therefore will require them to start the program all over again in order to gain sobriety (Ken & Kushner &Matt, 2013).
Conclusion
Alcohol use disorder is becoming rampant in the society. Different avenues should be used to educate and treat those affected by the disease. Therefore qualified specialist in the field should be able to identify every patient needs in order to treat them accordingly.
References
Asia News Monitor, (2015). United States: Learn to Recognize the Signs of an Alcohol Problem. Asia News Monitor; Bangkok. 12 May 2015.
Asia News Monitor (2015) United States: Marijuana vs. Alcohol: Which Is Really Worse for Your Health? Asia News Monitor: Bangkok. 07 Oct 2015.
Dennis, M., Victor, C., Mady, C., Brendan, S., (2013). Treating Alcohol and Drug Use Disorders/Alcohol and Drug Use: The Authors Reply. Health Affairs; Chevy Chase32.3. PP. 630.
Kattimani, S., Bharadwaj, B., (2013). Clinical management of alcohol withdrawal: A systematic review. Industrial Psychiatry Journal; Mumbai22.2. Pp. 100-108.
Lital, R., David, T., Harold, W., (2013). Exendin-4 induced glucagon-like peptide-1 receptor activation reverses behavioral impairments of mild traumatic brain injury in mice. Age. Dordrecht35.5. PP. 1621-36.
Mental Health Business Week, (2015). Patents; “Combination Treatment for Alcohol Dependent Patients” in Patent Application Approval Process (USPTO 20150209372). Mental Health Business Week; Atlanta. Aug 22, 2015: PP. 154.
Picci, R., Francesco, O., Marco, Z., et al (2014). Quality of life, alcohol detoxification and relapse: Is quality of life a predictor of relapse or only a secondary outcome measure? Quality of Life Research; Dordrecht23.10. PP. 2757-67.
Prakash, S., Neelu, S., Amool, S., et al (2015). Personality disorder, emotional intelligence, and locus of control of patients with alcohol dependence. Industrial Psychiatry Journal; Mumbai24.1. PP. 40-47.
Ritchie, S. J., Timothy, B. C; Corley, J., Geraldine, M., Davies, G., et al (2014). Alcohol consumption and lifetime change in cognitive ability: a gene × environment interaction study. Age; Dordrecht36.3:PP. 9638.
Winters, Ken C.W., Kushner, Matt, G.K., (2013). Treatment Issues Pertaining to Pathological Gamblers with a Comorbid Disorder. Journal of Gambling Studies, supply toward an Improved Understanding of Comorbidity: New York19.3. PP. 261-7.
We can write this or a similar paper for you! Simply fill the order form!




