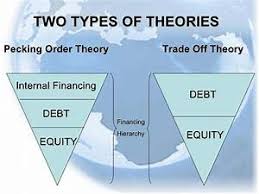
Trade-off and Pecking-order Theories
Order Instructions:
For this paper, the writer will have to read the two post and react to them in one paragraph each. The writer will expand and constructively challenge each of this postings using a minimum of one scholarly article to support his point. each posting respond must have a minimum of 250 words and APA must be use . The writer will respond directly on the uploaded paper with the respond coming directly under each posting as indicated. the references must be in APA format.
SAMPLE ANSWER
The writer must clearly relate to each post hear below constructively challenging or acknowledging the writer.
Trade-off and Pecking-order Theories
Several theories are proposed to explain how companies deal with debt and financial distress. After reviewing the resources for this week:
- Compare and contrast trade-off theory and pecking-order theory.
- Describe a specific business that seems to follow trade-off theory and another that follows pecking-order theory.
- Why would these theories be more applicable in some industries than others?
For this paper, the writer will have to read the two post and react to them in one paragraph each. The writer will expand and constructively challenge each of this postings using a minimum of one scholarly article to support his point. each posting respond must have a minimum of 250 words and APA must be use . The writer will respond directly on the uploaded paper with the respond coming directly under each posting as indicated. the references must be in APA format.
Post 1
In a one paragraph each expand and constructively challenge each of this postings, using a scholarly article to support your point on each paragraph
Trade Off and Pecking Order Theory
Compare and contrast trade-off theory and pecking-order theory
The Trade-off Theory or Static Trade-off Theory states that a firm’s capital structure decision involves a trade-off between the tax benefits of debt and the costs of financial stress. Firms choose their capital structures by trading off the benefits of debt financing such as tax shields, against the costs associated with financial distress and bankruptcy. The implication shows how each individual firm has an optimal amount of debt, which becomes the firm’s target debt level (Ross, Westerfield, & Jaffe, 2013). The company will choose how much debt to finance and how much equity to finance by balancing the costs and benefits of each. This theory shows how corporations are financed with debt and equity.
The Pecking Order Theory is a hierarchy or financing strategy in which using internally generated cash is at the top, issuing new equity is at the bottom, and issuing new debt is in the middle (Ross et al, 2013). Firms would prefer internal financing, and debt is preferred over equity if the firm has to result to external financing. When firm’s issue equity it means they have to bring external ownership into the company. These two theories are similar because they weight the benefits and costs between debt and equity using the debt ratio. The two theories are different because in the Trade-off Theory asset tangibility, profitability and tax shield are significant. In the Pecking Order Theory the most influential factors are long term profitability and investment opportunities (Vatavu, 2012).
Describe a specific business that seems to follow trade-off theory and another that follows pecking-order theory.
A business that follows the Trade-off Theory is one that is well established with enough equity generated in the firm. Microsoft is a business that could follow the trade off theory because it was not at its optimal capital structure and was not maximizing its value as an all equity firm. A business that follows the Pecking-order Theory is a smaller business. These businesses use their internal resources first before turning to lenders or investors to keep the business operational.
Why would these theories be more applicable in some industries than others?
These theories could be more applicable to some firms than others because the level of debt and equity in a firm plays a major significance. These theories apply to firm specific factors that show most significance in the capital structure of asset tangibility, size, investment opportunities, profitability, and tax shield (Vatavu, 2012).
References
Ross, S. A., Westerfield, R. W., & Jaffe, J. (2013). Corporate finance (10thed.). New York: McGraw-Hill Irwin.
Vatavu, S. (2012). Trade-off versus Pecking Order Theory in listed companies around the world.
Annals of the University of Petrosani Economics, 12(2), 285-292. Retrieved from
Write a one paragraph hear to expand and constructively challenge the above postings, using a scholarly article to support your point.
The trade off theory the optimal point where a firm’s use of debt and equity capital provides the greatest benefit to the organization in terms of the cost of capital. Using the Modigliani-Miller proposition II of the model, a company will enjoy the use of debt as a form of interest tax shield. The size of the company does not matter but the benefit obtained from using either the debt capital or equity (Modigliani and Miller, 1958).The cost of capital is weighted against the benefit of using either of the two or the proportion that derives the greatest benefit. Microsoft would have accumulated a lot of equity capital in its existence but its benefit compared to companies that have optimal debt-equity ratio may be deriving more benefit. The pecking order on the other hand proposes that the management of a company should use a source of capital that provides the most information or one which the company has more information on its source and application. This information would include the company’s business risks, the degree to which a company’s assets are tangible and the tax situation in a country. These means that companies should use equity capital. A company achieves the highest value when it utilizes 100% debt in its capital structure while at the same time its cost reduces to the lowest than when its financing its investment or development from equity capital. The US government occasionally offers zero-federal-plus-state corporate tax rate to promote investment in certain industries like in infant apparel manufacturing companies. These opportunities represent savings in terms of debt capital application.
References
Modigliani, F. and Miller, M. (1958) “The Cost of Capital, Corporation Finance, and the Theory of Investment,” American Economic Review, June, 48:3, 261–97.
Post 2
Capital Structure Theory
Capital structure determination poses a challenge to financial executives. Corporate leaders consider assets, profitability, size and debt when selecting a capital structure model. The purpose of this discussion is to compare and contrast trade-off and pecking-order capital structure theories.
Trade-off vs. Pecking-Order Theory
Trade-off and pecking-order theory are two capital structure options used by businesses. Financial leaders must determine the best methodology for funding capital projects, expansions, or meeting shareholder obligations. Trade-off theory states that a company balances the benefits of debt to increase capital with the risk of the cost of bankruptcy (Ross, Westerfield, & Jaffe, 2013; Vatavu, 2012). Conversely, pecking-order theory dictates a hierarchy decision process for raising capital where internal funding is the priority then debt financing (Guo&Leinberger, 2012; Ross et al., 2013). In a firm where leveraging debt provides a maximum tax benefit, the financial officer may choose a trade-off capital structure model whereas in a company with low-risk tolerance pecking order may be the most beneficial option.
Capital Structure Theory Application
Trade-off theory focuses on debt leverage for the purpose of raising capital. Large or established firms are most likely to employ the trade-off theory in their capital structure (Lopez-Gracia&Sogorb-Mira, 2008; Vatavu, 2012). Big companies have many assets along with stable revenue that allows for debt leverage tolerance. Businesses that are widely diversified such as Disney, also represent an example of a firm that employees trade-off theory in that the can take advantage of tax benefits because they have little risk of bankruptcy (Vatavu, 2012). Lopez-Gracia and Sogorb-Mira (2008) reviewed more than 3,500 small and moderate sized company’s capital structure and found that the consumer and manufacturing industries are most likely to employ the trade-off capital structure theory.
Pecking-order capital structure favors internal financing over external funding but like trade-off theory is not applicable to all companies. Small firms and new business are most likely to employ pecking-order theory because the tax shield benefits do not outweigh the cost and risk of debt leverage (Lopez-Gracia&Sogorb-Mira, 2008). Smaller firms who favor internal financing of projects and tech industry where the company has intangible assets utilize the pecking-order theory (Guo&Leinberger, 2012). Companies who cannot leverage debt or want to appear stronger may implement the pecking-order capital structure theory.
Rationale for Trade-off and Pecking-order Theories
The rationale for choosing one theory over another depends on the company type, size, and goals. Trade-off capital structure provides improved stability to balance debt and equity while funding capital budgets (Vatavu, 2012). Conversely, firms who are vulnerable, intolerant to risk, faced with high financing costs, or are in a growth phase benefit from pecking-order capital structure (Guo&Leinberger, 2012; Lopez-Gracia&Sogorb-Mira, 2008; Vatavu, 2012). The benefits of tax deductions may not be an advantage to the small or emerging company attempting to establish itself. Therefore, pecking-order is the optimal choice in the capital structure.
Conclusion
A capital structure theory selection must be pondered carefully. Business and financial leaders must choose a structure that fits the company’s size, operations, financial needs, and risk tolerance. Trade-off theory is best applied to businesses that are established, profitable and have tangible assets where debt leverage maximizes tax benefits to funding. Pecking-order theory, on the other hand, supports the smaller or emerging firm who prefer to finance through their internal equity and earnings. The goal of the capital structure is to provide funding for capital budgets therefore selecting a practice theory will enable a company to establish appropriate funding while remaining profitable.
References
Guo, E., &Leinberger, G. (2012). Firm growth and financial choices in Pennsylvania firms: An empirical study about the pecking order theory. Journal of Accounting and Finance, 12, 123-142. Retrieved from http://www.na-businesspress.com/jafopen.html
Lopez-Gracia, J., &Sogorb-Mira, F. (2008). Testing trade-off and pecking order theories financing SMEs. Small Business Economics, 31, 117-136. doi:10.1007/s11187-007-9088-4
Ross, S. R., Westerfield, R. W., & Jaffe, J. (2013). Corporate finance (10thed.). NY:McGraw-Hill.
Vatavu, S. (2012). Trade-off versus pecking order theory in listed companies around the world. Annals of the University of Petrosani, Economics, 12, 285-292. Retrieved from http://journals.indexcopernicus.com/abstracted.php?id=9345
Write a one paragraph hear to expand and constructively challenge the above postings, using a scholarly article to support your point.
The use of debt capital has mostly being applied to finance large projects that are beyond the company’s ability to finance through equity. The difference between using debt and equity in a company largely depends on a company’s liquidity and leverage status. Companies that are unstable financially prefer the pecking order while financially sound and stable companies would prefer the trade off. Other factors like the regulatory environment, the conditions and state of a country’s economy and the type of industry that the company is operating in have to be factored. For example, if the US government removes the tax benefit and the 40% federal-plus-state corporate tax is fully implemented, companies would think again about the trade-off especially the small industries. In my opinion, the relative issue between the pecking order and the trade-off in these case is that the debt holders are in most cases particularly concerned with the company’s ability to repay the debt and they are represented by the group that advocates for the pecking order while the shareholders are concerned with the ability of the firm earning big income hence the group that supports the tradeoff issue. A successful shareholder will earn more by investing in risky projects but the debt holder will only earn his return whether the project fails or succeed (Myers, 1984, pg 16). The pecking order concept claims that companies prefer equity financing as it involves the use of the relatively safe retained earnings that bears no risks compared to the risky external financing that also involves the disclosure of a lot of information on the company prospectus.
References
Myers, S. (1984)”The Search for Optimal Capital Structure,” Midland Corporate Finance Journal, 1 spring, 6-16
We can write this or a similar paper for you! Simply fill the order form!




