Nash Equilibrium Conditions following Single Strategy Table A (Firm 1) S1a S1b (firm2)S2a 2, 2 3, 0 S2b 0, 3 1, 1 Table B (Firm 1) S1a S1b (firm2)S2a 10, 10 16, 4 S2b 18, 2 4, 16
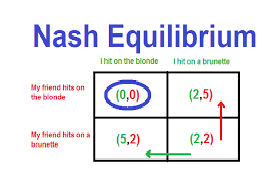
1, if there is a Nash (non-cooperative) equilibrium following a single strategy, identify it and demonstrate that it is Nash equilibrium 2, if there is no single strategy that satisfies the Nash equilibrium conditions, demonstrate that and calculate and explain the strategy mix. Nash Equilibrium is a term used in game theory to describe an equilibrium where each player’s strategy is optimal given the strategies of all other players. A Nash Equilibrium exists when there is no unilateral profitable deviation from any of the players involved. In other words, no player in the game would take a different action as long as every other player remains the same. Nash Equilibria are self-enforcing; when players are at a Nash Equilibrium they have no desire to move because they will be worse off.




