The role of the HR leader in CSR
Order Instructions:
Dear Admin,
I need an essay in the following subject:
The role of the HR leader in CSR
CSR will remain a lofty ideal with no practical impact if organisational leaders do not take responsibility for its implementation. As with other strategic aspects of organisations, CSR planning and implementation is often a joint effort of leaders in many roles, including the HR leader. In this week’s Collaboration, you will continue your discussion on the nature and value of CSR, expanding your dialogue on the role of HR professionals in CSR.
a)Search for examples of CSR online and for additional scholarly research on CSR, focusing on the role of HR.
b)Critically analysing the CSR-related HRM practices of organisations with which you are familiar or which you have researched online.
c)Synthesising general lessons about the HR leader’s role in, and responsibility for, promoting, planning for and implementing CSR
d)Discussing the ability of CSR to enable HR leaders to address ethical and cultural issues within an organisation
Also, the following conditions must meet in the essay:
1) The answer must raise appropriate critical questions.
2) The answer must include examples from aviation experience or the web with references from relevant examples from aviation companies.
3) Do include all your references, as per the Harvard Referencing System,
4) Please don’t use Wikipedia web site.
5) I need examples from peer reviewed articles or researches.
Note: To prepare for this essay please read the required articles that is attached
Appreciate each single moment you spend in writing my paper
Best regards
SAMPLE ANSWER
The role of the HR leader in CSR
As the function of human resource department in a company continues to expand and human resource personnel become more entrenched in the business strategy in many organizations across the United Kingdom, CSR can have considerable implications for the HR profession. In this paper, a discussion of the role of the human resource (HR) professionals in corporate social responsibility (CSR) is provided. A critical analysis of the CSR-related human resource management practices of organizations in the aviation industry is also provided. Moreover, this paper discusses the general lessons about the role of the HR in, and responsibility for, promoting, planning for, and implementing CSR as well as the ability of CSR to enable HR leaders to address both cultural and ethical issues within an organization.
Cohen, Taylor & Camen (2011, p. 15) pointed out that the commitment of an organization to CSR is a component of both customer brand and the employment brand. Human resource professionals have embraced it and use it as a tool when retaining existing talent or recruiting new talent to the company. HR departments play a vital role in making sure that the organization adopts CSR programs. In addition, the human resource department can manage the corporate social responsibility plan implementation and proactively monitor its espousal, whilst noting and celebrating its success in the organization (Preuss, Haunschild & Matten 2009, p. 973).
Successful corporate social responsibility calls for a clearly expressed mission statement, vision, as well as values. The human resource leader could endorse or initiate the upgrading or development of a values, mission, and vision foundation if one is lacking or if it exists but does not address corporate social responsibility in an explicit manner (Cohen, Taylor & Camen 2011, p. 16). For the foundation to foster alignment, it should include elements of CSR or sustainability. Where a corporate social responsibility ethic is yet to take hold, the HR leader could support the need and opportunity for a mission, vision, and a set of values for the company and explain the way it could add return on investment to the company; that is, why this can be a good people strategy and a good business strategy at the same time (Guerci et al. 2015, p. 328). The HR leader can inform the organization’s board and senior executives about the opportunity and what it means and the reason why it actually makes good business sense. In essence, these are the initial steps to building corporate social responsibility into the DNA of the company and into the strategic and operating framework of the company (Voegtling & Greenwood 2013, p. 66).
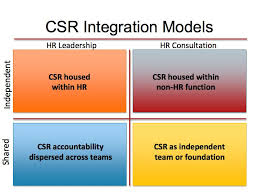
The moment the mission, vision, and values framework is clear, the company is now set to take on the development of its corporate social responsibility strategy. At this stage, the HR leader’s role is of major importance to every step. HR professionals have a significant people perspective to contribute and they would be involved in the implementation of the main measures (Morgeson et al. 2011, p. 287). In organizations in which corporate social responsibility is housed within the HR department, the HR leader has a central role in the development of CSR strategy. The HRM manager is a strategic partner in the company; hence he or she can assist in driving the formulation of the corporate social responsibility strategy.
Lis (2012, p. 282) stated that not every business organization has the resources – personnel, time, and money – to funnel corporate social responsibility programs. Nonetheless, these CSR initiatives may not be costly or may not necessitate a commitment of too much time. Companies which are interested in corporate social responsibility can decide to begin with small projects which demonstrate their dedication to the community and their staffs. Human resource managers could address a challenge such as this one by considering various options and coming up with ingenious approaches to Corporate Social Responsibility to present to their organization. For instance, they can consider partnering with other companies such as a co-sponsor (Mankelow 2008, p. 2177). Thus, the HR leadership as the company’s ears and eyes is critical to the corporate social responsibility equation. It is notable that through properly-managed policies, programs, and practices, HR has the opportunity of engaging the company’s top management and the company’s stakeholders in the value of CSR. It can do this by focusing on employee relations, community relations, communications, safety, and health to offer their companies a competitive advantage. Lis (2012, p. 291) stated that HR managers can influence 3 key CSR standards – community involvement, employment practices, and ethics – which relate either in an indirect or direct way to the local community, clients/customers, or staff members. By taking into consideration these 3 corporate social responsibility standards, HR managers can then recognize their company’s CSR stage prior to making decisions to develop and carry out corporate social responsibility initiatives.
An example of the critical role of the HR leader in CSR in the aviation industry is as regards Air Greenland. Air Greenland takes CSR very seriously. This airline is committed to creating a common value for the company and the society in everything it does. As such, Air Greenland chose to call its Corporate Social Responsibility approach We bring Greenland forward (Air Greenland 2013). With viability, reputation, and at times survival of the organization at stake, the HR leadership at Air Greenland undertook the critical role of spearheading the development as well as strategic execution of corporate social responsibility throughout the company and promoting sound corporate citizenship. Air Greenland understands that a fundamental barrier to Greenland’s development is the lack of skills and competencies (Air Greenland 2013). For that reason, this airline is actually committed to developing competence throughout the organization as well as to supporting education more generally outside the organization. Moreover, this airline is committed to skills and competence development of its staffs in a balance between the staffs own wishes and the needs of the airline (Air Greenland 2013). In this regard, the HR department at Air Greenland manages the corporate social responsibility plan execution and the HR leader proactively monitors its adoption, whilst noting and celebrating its success organization wide.
CSR initiatives and programs are able to enable HR leaders to address ethical and cultural issues within an organization. As part of HR initiatives related to ensuring the inclusion of employees from diverse cultures, HR managers would recruit and employ individuals of different cultural backgrounds. HR leaders are also vital in the development and implementation of ethical practices and standards in dealings with every stakeholder of the organization. HR leaders explicitly communicate the organization’s commitment to ethical conduct and ensure that all employees strictly uphold ethical conduct in the organization (Preuss, Haunschild & Matten 2009, p. 962).
Conclusion
To sum up, HR departments in many organizations play an imperative role in making sure that their organizations adopt corporate social responsibility initiatives. The HR manager is a strategic partner in the business organization and can be of assistance in driving the development of the corporate social responsibility strategy. Through properly-managed policies, programs, and practices, the HR leader can engage the company executives and stakeholders in the value of Corporate Social Responsibility for instance focusing on worker relations, community relations, communications, safety, and even health so as to offer their firms a competitive advantage in the marketplace.
References
Air Greenland 2013, Corporate Social Responsibility (CSR) Policy for Air Greenland. Retrieved from https://www.airgreenland.com/media/522581/corporate-social-responsibility-policy-air-greenland-signatures.pdf
Cohen, E., Taylor, S., & Camen, MM 2011, HR’s Role in Corporate Social Responsibility and Sustainability. Coventry, England: Cengage Learning.
Guerci, M, Radaelli, G, Siletti, E, Cirella, S, & Rami Shani, A 2015, ‘The Impact of Human Resource Management Practices and Corporate Sustainability on Organizational Ethical Climates: An Employee Perspective’, Journal Of Business Ethics, 126, 2, pp. 325-342, Business Source Complete, EBSCOhost, viewed 6 February 2015.
Lis, B 2012, ‘The Relevance of Corporate Social Responsibility for a Sustainable Human Resource Management: An Analysis of Organizational Attractiveness as a Determinant in Employees’ Selection of a (Potential) Employer’, Management Revue, 23, 3, pp. 279-295, Business Source Complete, EBSCOhost, viewed 6 February 2015.
Mankelow, G 2008, ‘Social responsibility paradox of small business human resource management practices’, International Journal Of Human Resource Management, 19, 12, pp. 2171-2181, Business Source Complete, EBSCOhost, viewed 6 February 2015.
Morgeson, F, Aguinis, H, Waldman, D, Siegel, D, Kraimer, M, Takeuchi, R, & Frese, M 2011, ‘Special Issue Call for Papers: Corporate Social Responsibility and Human Resource Management/Organizational Behavior’, Personnel Psychology, 64, 1, pp. 283-288, Business Source Complete, EBSCOhost, viewed 6 February 2015.
Preuss, L, Haunschild, A, & Matten, D 2009, ‘The rise of CSR: implications for HRM and employee representation’, International Journal Of Human Resource Management, 20, 4, pp. 953-973, Business Source Complete, EBSCOhost, viewed 6 February 2015.
Voegtling, C., & Greenwood, M 2013, CSR AND HRM: A Review and Conceptual Analysis. Academy Of Management Annual Meeting Proceedings, 65-70. doi:10.5465/AMBPP.2013.21
We can write this or a similar paper for you! Simply fill the order form!