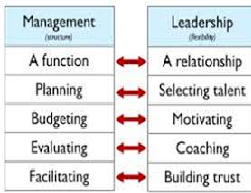
Combining Nurse Leader With Advocacy Order Instructions: Combining Nurse Leader With Advocacy
View Rubric Details: Rate yourself using the results from the “Nurse Manager Skills Inventory”:
http://www.aacn.org/wd/practice/docs/nurse-manager-inventory-tool.pdf
Write a reflection of 750-1,000 words in which you identify your strengths and weaknesses related to the four content areas below:
1.Personal and professional accountability
2.Career planning
3.Personal journey disciplines
4.Reflective practice reference behaviors/tenets
Discuss how you will use your current leadership skill set to advocate for change in your workplace.
Identify one personal goal for your leadership growth and discuss your implementation plan to achieve that goal.
While APA format is not required for the body of this assignment, solid academic writing is expected and in-text citations and references should be presented using APA documentation guidelines, which can be found in the APA Style Guide, located in the Student Success Center.
This assignment uses a rubric. Please review the rubric prior to beginning the assignment to become familiar with the expectations for successful completion.
You are required to submit this assignment to Turnitin. Please refer to the directions in the Student Success Center
Rubric
Combining Nurse Leader With Advocacy
1
Unsatisfactory
0.00%
2
Less than Satisfactory
75.00%
3
Satisfactory
79.00%
4
Good
89.00%
5
Excellent
100.00%
80.0 %Content
30.0 % Identification of strengths and weaknesses related to the four content areas below: 1) personal and professional accountability; 2) career planning; 3) personal journey disciplines, and 4) reflective practice reference behaviors/tenets. (Source: AONE)
Provides strengths and/or weaknesses based on some of the listed content areas.
Lists strengths and weaknesses based on each of the listed content areas, but does not draw on evidence from the given Web site.
Lists strengths and weaknesses based on each of the listed content areas and draw on evidence from the given Web site for some of the content areas.
Lists strengths and weaknesses based on each of the listed content areas and draw on evidence from the given Web site.
Lists and analyzes strengths and weaknesses based on each of the listed content areas, and draws on evidence from the given Web site.
25.0 % Discussion of use of current leadership skills to advocate change in the workplace.
Fails to mention either change in the workplace and/or personal skill set.
Discusses one change that can be made in the workplace, without providing examples or evidence. Makes brief mention of personal skill set, but does not effectively demonstrate how it can be used to effect change.
Discusses one change that can be made in the workplace, without providing examples or evidence. Evaluates how personal skill set can be used to effect change in the workplace.
Discusses one change that can be made in the workplace, while giving a clear and relevant example for why the change is necessary. Evaluates how personal skill set can be used to effect change in the workplace.
Discusses specific changes that can be made in the workplace are discussed while giving clear and relevant examples of why changes are necessary. Evaluates how personal skill set can be used to effect change in the workplace.
25.0 % Reflection on a personal goal for leadership growth and development of implementation plan to reach the goal.
Pinpoints a goal for leadership growth, but does not provide a plan for attaining the goal.
Pinpoints a goal for leadership growth, but the plan for attaining the goal is not aligned to the final outcome.
Provides a surface-level reflection on areas of growth. Pinpoints at least one specific goal for leadership growth, but provides an oversimplified plan for attaining the goal.
Reflects on areas for growth. Pinpoints at least one specific goal for leadership growth, and outlines a clear implementation plan to meet the goal.
Provides a thoughtful reflection on areas for growth. Pinpoints at least one specific goal for leadership growth, and outlines a well-organized and realistic implementation plan to meet the goal.
15.0 %Organization and Effectiveness
5.0 % Thesis Development and Purpose
Paper lacks any discernible overall purpose or organizing claim.
Thesis and/or main claim are insufficiently developed and/or vague; the purpose is not clear.
Thesis and/or main claim are apparent and appropriate to the purpose.
Thesis and/or main claim are clear and forecast the development of the paper. It is descriptive and reflective of the arguments and appropriate to the purpose.
Thesis and/or main claim are comprehensive; contained within the thesis is the essence of the paper. Thesis statement makes the purpose of the paper clear.
15.0 %Organization and Effectiveness
5.0 % Paragraph Development and Transitions
Paragraphs and transitions consistently lack unity and coherence. No apparent connections between paragraphs are established. Transitions are inappropriate to purpose and scope. The organization is disjointed.
Some paragraphs and transitions may lack logical progression of ideas, unity, coherence, and/or cohesiveness. Some degree of organization is evident.
Paragraphs are generally competent, but ideas may show some inconsistency in the organization and/or in their relationships to each other.
A logical progression of ideas between paragraphs is apparent. Paragraphs exhibit a unity, coherence, and cohesiveness. Topic sentences and concluding remarks are appropriate to the purpose.
There is a sophisticated construction of paragraphs and transitions. Ideas progress and relate to each other. Paragraph and transition construction guide the reader. Paragraph structure is seamless.
15.0 %Organization and Effectiveness
5.0 % Mechanics of Writing (includes spelling, punctuation, grammar, language use)
Surface errors are pervasive enough that they impede communication of meaning. Inappropriate word choice and/or sentence construction are used.
Frequent and repetitive mechanical errors distract the reader. Inconsistencies in language choice (register), sentence structure, and/or word choice are present.
Some mechanical errors or typos are present but are not overly distracting to the reader. Correct sentence structure and audience-appropriate language are used.
The prose is largely free of mechanical errors, although a few may be present. A variety of sentence structures and effective figures of speech are used.
The writer is clearly in command of standard, written, academic English.
5.0 %Format
2.0 % Paper Format (1- inch margins; 12-point-font; double-spaced; Times New Roman, Arial, or Courier)
The template is not used appropriately or documentation format is rarely followed correctly.
The template is used, but some elements are missing or mistaken; lack of control with formatting is apparent.
The template is used, and formatting is correct, although some minor errors may be present.
The template is fully used; There are virtually no errors in formatting style.
All format elements are correct.
5.0 %Format
3.0 % Research Citations (In-text citations for paraphrasing and direct quotes, and reference page listing and formatting, as appropriate to assignment)
No reference page is included. No citations are used.
The reference page is present. Citations are inconsistently used.
The reference page is included and lists sources used in the paper. Sources are appropriately documented, although some errors may be present.
The reference page is present and fully inclusive of all cited sources. Documentation is appropriate and GCU style is usually correct.
In-text citations and a reference page are complete. The documentation of cited sources is free of error.
100 % Total Weightage
Combining Nurse Leader With Advocacy Sample Answer
Combining Nurse Leader with Advocacy
Introduction
The Nurse Manager Skills inventory helps one realize their strengths and weaknesses in the nursing profession in order to maximize on their effectiveness as leaders. It is important for nurses to take the test from time to time so as to realize their potential. Nurses are often expected to offer servant leadership while at work. Every patient desires a mentor, a friend and a professional treating them as they continue in their recovery journey (Baxter & Warshawsky, 2014). Nurses offer these services in an all-inclusive package and often stretch beyond the limits of the caregiver assignment they are tasked with. I took the Nurse Manager Skills Inventory test and realized several aspects of my profession that I was not aware of from the onset of my career.
Personal and Professional Accountability
I ranked fairly average on personal and professional accountability. With regards to personal accountability, the issues of personal life and life beyond work were evaluated. These tore right at the very center of my values. I realized that a nurse is supposed to be a leader and worker at the same time. This is due to the numerous decisions we have to make in our line of work every day. It is important to realize a perspective that guides one’s life even when they are not working. Professional conduct must thus be upheld at all time. The desire to do right must also not impede on professional judgment. I had some of these aspects within my personality but some; I did not.
Career Planning
I ranked very low with regard to career planning. The goals of my career, my ambitions for growth and the path I would take to get there were not very clear. It got me thinking that I should do more to support my career ambitions and future plans. Of more importance to me is the ability to guarantee that I am able to foresee growth not only in the working environment but in myself as well. It is very critical to know this since as a nurse, there is a lot one can do and that needs to be done. However, a combination of the right skill set and mentorship as well as the right environment to grow one’s career is important (Baxter & Warshawsky, 2014). Nevertheless, as a dependable entity among society, one has to consider the needs of the society as well.
Personal Journey Disciplines
Over the course of my career, I have grown fond of my patients and realized that to me they were like family. I thus have never considered my family more important than this work and they have had to understand my professional ethics. I have learned to talk to patients better and offer consolation where necessary and truth was inevitable. All in all; I have grown to become a professionally ethical caregiver. I still continue to learn from my peers and superiors, but the strength that keeps me going is the passion for my assignments.
Reflective Practice Reference Behaviors/Tenets
Based on past experiences, I have been able to grow my professional discretion and opinion on matters. Aspects of treatment that were not known to me have often been realized right at the center of a treatment trial, vaccination, or surgical procedure. Past practice work from published nurses has also been of guide to me over the years. It is often difficult to get the exposure one needs but combining experience from circumstances we go through at work as well as the published work from reputable and peer-reviewed sources makes nursing more accurate and professional (Baxter & Warshawsky, 2014). I have been a good student in reflective practice and indeed continue to do so to date.
Applying My Leadership Skills at the Workplace
The working environment I am in requires more of a servant leadership approach. There is a need for a leader to exercise a lot of patience and take into consideration the needs, aspirations, and feelings of the staff. I believe that as a leader, the hospital requires a proper understanding of the welfare of all nurses. We need to always consider the nurse (employee) as the most critical resource in the institution. For this reason; we have to always listen to their problems and counsel them from time to time. I also would encourage nurses to pursue learning as a way to improve the practice. This would be done by enrolling into more classes and conducting periodical research on epistemology.
For my leadership growth, I intend to be time conscious by respecting deadlines and doing the right thing at the right time. Lately, I have encountered challenges of rushing to meet deadlines. This makes my work stressful since I end up completing projects not with the same satisfaction as I had intended. For implementation, I plan to develop a time table outlining my daily schedule. I will endeavor to follow the timetable to the latter so that I can be a reputable lender that is an example to others.
Combining Nurse Leader With Advocacy Conclusion
As a leader, I hope to become more in tune with the latest technologies in the medical field. I seek to be more aware of new infections and spiraling health threats within my community and the country at large. I also seek to be more informed on what research is being done to realize an end to the incurable diseases afflicting the world. I will thus be a research-centric leader who always seeks to find a breakthrough in treatment methods and techniques. I believe that by leading nurses in research, we can share a global platform with every nurse especially in the developing world to assist them to deal with significant health threats in their communities.
Combining Nurse Leader With AdvocacyReference
Baxter, C., & Warshawsky, N. (2014). Exploring the Acquisition of Nurse Manager Competence. Nurse Leader, 1246, 59-51, 59.